-
- 1
- Y. Boykov, O. Veksler,
and R. Zabih.
Fast approximate energy minimization via graph cuts.
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 23(11):1222-1239, 2001.
- 2
- G. Wei, W. Brauer, and
G. Hirzinger.
Intensity- and gradient-based stereo matching using hierachcial
gaussian basis functions.
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 20:1143-1160, 1998.
- 3
- M. J. Hannah.
Digital stereo image matching techniques.
Archives on Photogrammetry and Remote
Sensing, 27:280-293, 1988.
- 4
- D. Scharstein and
R. Szeliski.
A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence
algorithms.
Int. J. Comput. Vision,
47(1-3):7-42, 2002.
- 5
- T. Poggio, V. Torre,
and C. Koch.
Computational vision and regularization
theory, pages 472-491.
Artificial intelligence at MIT: Expanding Frontiers. MIT Press,
Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990.
- 6
- J. Marroquin,
S. Mitter, and T. Poggio.
Probabilistic solution of ill-posed problems in computational vision.
J. of American Statistical Association,
82:76-89, 1987.
- 7
- D. Marr and T. Poggio.
Cooperative Computation of Stereo
Disparity, pages 432-461.
Artificial intelligence at MIT: Expanding Frontiers. MIT Press,
Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996.
- 8
- G. Gimel'farb, V. B.
Marchenko, and V. Rybak.
An algorithm for automatic identification of identical sections on
stereopair photographs.
Cybernetics [translation from Russian],
2:118-129, 1972.
- 9
- H. H. Baker.
Depth from edge and intensity based
stereo.
PhD thesis, University of Illinois, 1981.
- 10
- W. E. L. Grimson.
From images to surfaces,
pages 132-151.
Artificial intelligence at MIT: Expanding Frontiers. MIT Press,
Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996.
- 11
- J. Liu and
G. Gimel'farb.
Accuracy of stereo reconstruction by minimum cut, symmetric dynamic
programming, and correlation.
In Proc. Image Vision Computing New Zealand Conf (IVCNZ),
Akaroa, New Zealand, November 2004, pages 65-70, 2004.
- 12
- P. Leclercq, J. Liu,
M. Chan, A. Woodward, G. Gimel'farb, and
P. Delmas.
Comparative study of stereo algorithms for 3D face reconstruction.
In Proc. Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems
Conf., Brussel, Belgium, 2004, pages 201-208, 2004.
- 13
- P. Leclercq, J. Liu,
A. Woodward, and P. Delmas.
Which stereo matching algorithm for accurate 3D face creation?
In Proc. Int. Workshop on Combinatorial Image Analysis
(IWCIA), Auckland, New Zealand, 2004, pages 690-704, 2004.
- 14
- J. Morris,
G. Gimel'farb, J. Liu, and P. Delmas.
Concurrent stereo matching: An image noise-driven model.
In Proc. 5th Int. IAPR Workshop on Energy Minimization
Methods in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (EMMCVPR),
St.Augustine, Florida, USA, November 2005, volume 3757 of Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 307-317. Springer Berlin,
2005.
- 15
- P. Delmas,
G. Gimel'farb, J. Liu, and J. Morris.
A noise-driven paradigm for solving the stereo correspondence problem.
In Proc. Mexican Int. Conf. on Artificial Intelligence
(MICAI), Monterrey, Nuevo Leon, Mexico, November 14-18 2005,
volume 3789 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
pages 307-317. Springer Berlin, 2005.
- 16
- J. Liu, P. Delmas,
G. Gimel'farb, and J. Morris.
Stereo reconstruction using an image noise model.
In Proc. Int. Conf. on Digital Image Computing: Techniques
and Applications, DICTA 2005, 6-8 December 2005, Cairns, Australia,
pages 69-75. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, 2005.
- 17
- G. Gimel'farb,
J. Morris, P. Delmas, and J. Liu.
Noise-driven symmetric concurrent stereo matching.
In Proc. Image Vision Computing New Zealand Conf. (IVCNZ),
Dunedin, New Zealand, November 2005, pages 90-95, 2005.
- 18
- G. Gimel'farb,
J. Morris, P. Delmas, and J. Liu.
Symmetric concurrent stereo under photometric image distortions.
In Proc. Int. Conf. on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Hong
Kong, China, August 2006. IEEE Computer Society, Los
Alamitos, 2006 [in print].
- 19
- M. Z. Brown,
D. Burschka, and G. D. Hager.
Advances in computational stereo.
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 25(8):993-1008, 2003.
- 20
- S. T. Barnard and M. A.
Fischler.
Computational stereo.
ACM Computing Surveys,
14:553-572, 1982.
- 21
- U. R. Dhond and J. K.
Aggarwal.
Structure from stereo - a review.
IEEE Trans. Systems, Man, and
Cybernetics, 19:553-572, 1989.
- 22
- L. L. Grewe and A. C.
Kak.
Stereo vision, pages
239-317.
Handbook of Pattern Recongnition and Image Processing. Academic Press,
New York, 1994.
- 23
- T.Ozanian.
Approaches for stereo matching: a review.
Modeling Identification Control,
16:65-94, 1995.
- 24
- G. A. Jones.
Constraint, optimization, and hierarchy: Reviewing stereoscopic
correspondence of complex features.
Computer Vision and Image
Understanding: CVIU, 65(1):57-78, 1997.
- 25
- J. Y. Goulermas.
Evolutionary techniques for the stereo
correspondence problem.
PhD thesis, Control System Centre, University of Manchester, Inst. Sci.
Technology, Manchester, U.K., 2000.
- 26
- U. V. Helava.
Object-space least-square correlation.
Photogrammetric Eng. Remote Sensing,
54:711-714, 1988.
- 27
- T. Kanade and
M. Okutomi.
A stereo matching algorithm with an adaptive window: Theory and
experiment.
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 16(9):920-932, 1994.
- 28
- C. L. Zitnick and
T. Kanade.
A cooperative algorithm for stereo matching and occlusion detection.
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 22(7):675-684, 2000.
- 29
- Y. Zhang and
C. Kambhamettu.
Stereo matching with segmentation-based cooperation.
In Proc. 7th European Conf. on Computer Vision-Part II,
London, UK, 2002, pages 556-571. Springer Verlag, 2002.
- 30
- G. Gimel'farb and
U. Lipowezky.
Accuracy of computational stereo: symmetric dynamic programming versus
correlation.
In Proc. Workshop on Pattern Recognition in Remote Sensing,
Niagara Falls, August 2002, Ontario, Canada, pages 49-56.
BPRA, 2002.
- 31
- G.V.S Raju, T. Binford, and
S. Shekar.
Stereo matching using Viterbi algorithm.
In Proc. DARPA Image Understanding Workshop, San Diego, CA,
USA, 1987, volume 2, pages 766-776, 1987.
- 32
- Y. Ohta and T. Kanade.
Stereo by intra- and inter-scanline search using dynamic programming.
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 7:139-154, 1985.
- 33
- S. A. Lloyd.
Stereo matching using intra- and inter-row dynamic programing.
Pattern Recognition Letters,
4:273-277, 1986.
- 34
- A. F. Bobick and S. S.
Intille.
Large occlusion stereo.
Int. J. Computer Vision,
33(3):181-200, 1999.
- 35
- S. S. Intille and A. F.
Bobick.
Disparity-space images and large occlusion stereo.
In Proc. 3th European conf. on Computer Vision, Stockholm,
Sweden, 1994, pages 179-186. Springer Verlag, 1994.
- 36
- D. Geiger,
B. Ladendorf, and A. Yuille.
Occlusions and binocular stereo.
Int. J. Comput. Vision,
14(3):211-226, 1995.
- 37
- I. J. Cox, S. L.
Hingorani, S. B. Rao, and B. M. Maggs.
A maximum likelihood stereo algorithm.
Computer Vision Image Understanding,
63(3):542-567, 1996.
- 38
- P. N. Belhumeur and
D. A. Mumford.
A Bayesian treatment of the stereo correspondence problem using
half-occluded regions.
In Proc. IEEE Computer Society Conf. on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Champaign, Illinois, 1992, pages
506-512. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, 1992.
- 39
- G. Gimel'farb.
Stereo terrain reconstruction by dynamic programming.
Handbook of Computer Vision and
Applications 2: Signal Processing and Pattern Recognition,
pages 505-530, 1999.
- 40
- G. Gimel'farb.
Probabilistic regularisation and symmetry in binocular dynamic
programming stereo.
Pattern Recognition Letters,
23(4):431-442, 2002.
- 41
- L. R. Ford and D. R.
Fulkerson.
Flows in Networks.
Princeton University Press, 1962.
- 42
- S. Geman and D. Geman.
Stochastic relaxation, gibbs distributions, and the bayesian
restoration of images.
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 6:721-741, 1984.
- 43
- J. P. P. Starink and
E. Backer.
Finding point correspondences using simulated annealing.
Pattern Recognition Letters,
28:231-240, 1995.
- 44
- D. M. Greig, B. T.
Porteous, and A. H. Seheult.
Exact maximum a posteriori estimation for binary images.
J. Royal Statistical Society, Ser. B.,
51:271-279, 1989.
- 45
- S. Roy and I. J. Cox.
A maximum-flow formulation of the n-camera stereo correspondence
problem.
In Proc. 6th Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), Bombay,
India, January 1998, pages 492-502, 1998.
- 46
- H. Ishikawa and
D. Geiger.
Occlusions, discontinuities, and epipolar lines in stereo.
In Proc. 5th European Conf. on Computer Vision-Volume I,
London, UK, 1998, pages 232-248. Springer Verlag, 1998.
- 47
- Y. Boykov, O. Veksler,
and R. Zabih.
Markov random fields with efficient approximations.
In Proc. IEEE Computer Society Conf. on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 1998,
pages 648-661. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, 1998.
- 48
- Y. Boykov, O. Veksler,
and R. Zabih.
Approximate energy minimization with discontinuities.
In Proc. IEEE Workshop on Energy Minimization Methods in
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (EMMCVPR), York, UK, July 26-29
1999, pages 205-220. Springer Berlin, 1999.
- 49
- O. Veksler.
Efficient Graph-Based Energy
Minimization Methods in Computer Vision.
PhD thesis, Cornell University, 1999.
- 50
- V. Kolmogorov and
R. Zabih.
Computing visual correspondence with occlusions via graph cuts.
In Proc. Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), Vancouver,
Canada July 9-12, 2001, pages 508-515, 2001.
- 51
- Y. Boykov and
V. Kolmogorov.
An experimental comparison of min-cut / max-flow algorithms for energy
minimization in vision.
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 26(9):1124-1137, 2004.
- 52
- P. F. Felzenszwalb and
D. P. Huttenlocher.
Efficient belief propagation for early vision.
In Proc. IEEE Computer Society Conf. on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Washington, DC, USA, 2004, pages
261-268. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, 2004.
- 53
- J. Sun, N. N. Zheng,
and H. Y. Shum.
Stereo matching using belief propagation.
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 25(7):787-800, 2003.
- 54
- J. Sun, Y. Li,
S. B. Kang, and H. Y. Shum.
Symmetric stereo matching for occlusion handling.
In Proc. IEEE Computer Society Conf. on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Diego, CA, USA, June 20-25 2005,
pages 399-406. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, 2005.
- 55
- Q. Yang, L. Wang,
R. Yang, H. Stewnius, and D. Nistr.
Stereo matching with color-weighted correlation, hierarchical belief
propagation and occlusion handling.
In Proc. IEEE Computer Society Conf. on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New York, USA, June 17-22 2006,
pages 2347-2354. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, 2006.
- 56
- A. Klaus, M. Sormann,
and K. Karner.
Segment-based stereo matching using belief propagation and a
self-adapting dissimilarity measure.
In Proc. Int. Conf. on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Hong
Kong, China, August 2006, 2006 [in print].
- 57
- H. Saito and M. Mori.
Application of genetic algorithms to stereo matching of images.
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 16(8):815-821, 1995.
- 58
- M. Gong and Y. H. Yang.
Genetic-based stereo algorithm and disparity map evaluation.
Int. J. Computer Vision,
47(1-3):63-77, 2002.
- 59
- S. Baker, R. Szeliski,
and P. Anandan.
A layered approach to stereo reconstruction.
In Proc. IEEE Computer Society Conf. on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, June 23-25 1998,
pages 434-441. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, 1998.
- 60
- S. Birchfield and
C. Tomasi.
Multiway cut for stereo and motion with slanted surfaces.
In Proc. 7th Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), Kerkyra,
Greece, 1999, pages 489-495, 1999.
- 61
- M. H. Lin and
C. Tomasi.
Surfaces with occlusions from layered stereo.
In Proc. IEEE Computer Society Conf. on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Madison, WI, USA, June 16-22 2003,
pages 710-717. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, 2003.
- 62
- H. Tao and H. Sawhney.
Global matching criterion and color segmentation based stereo.
In Proc. Workshop on the Application of Computer Vision
(WACV), Palm Springs, California, USA, December 4-6 2000,
pages 246-253, 2000.
- 63
- H. Tao, H. S. Sawhney,
and R. Kumar.
A global matching framework for stereo computation.
In Proc. Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), Vancouver,
Canada July 9-12, 2001, pages 532-539, 2001.
- 64
- M. Bleyer and
M. Gelautz.
A layered stereo matching algorithm using image segmentation and global
visibility constraints.
ISPRS J. Photogrammetry and Remote
Sensing, 59(3):128-150, May 2005.
- 65
- D. Comaniciu and
P. Meer.
Mean shift: A robust approach toward feature space analysis.
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 24(5):603-619, 2002.
- 66
- D. Comaniciu and
P. Meer.
Robust analysis of feature spaces: color image segmentation.
In Proc. IEEE Computer Society Conf. on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Juan, Puerto Rico, 1997,
pages 750-755. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, 1997.
- 67
- H. H. Baker.
Surfaces from mono and stereo images.
Photogrammetria, 39:217-237,
1984.
- 68
- G. Gimel'farb.
Intensity-based computer binocular stereo vision: signal models and
algorithms.
Int. J. Imaging Systems and Technology,
3(4):189-200, 1991.
- 69
- J. Kim, V. Kolmogorov,
and R. Zabih.
Visual correspondence using energy minimization and mutual information.
In Proc. 9th Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), Nice,
France, October 2003, pages 1033-1040, 2003.
- 70
- P. Leclercq and
J. Morris.
Assessing stereo algorithm accuracy.
In Proc. Image Vision Computing New Zealand Conf. (IVCNZ),
Auckland, New Zealand, 2002, pages 110-115, 2002.
- 71
- P. Leclercq and
J. Morris.
Robustness to noise of stereo matching.
In proc. Int. Conf. on Image Analysis and Processing
(ICIAP), Mantova, Italy, September 17-19 2003, pages
606-612. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, 2003.
- 72
- S. Roy.
Stereo without epipolar lines: A maximum-flow formulation.
Int. J. Computer Vision,
34(2-3):147-161, 1999.
- 73
- M. F. Tappen and W. T.
Freeman.
Comparison of graph cuts with belief propagation for stereo, using
identical MRF parameters.
In Proc. 9th Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), Nice,
France, October 2003, pages 900-907, 2003.
- 74
- Y. C. Hsieh, D. M.
McKeown, and F. P. Perlant.
Performance evaluation of scene registration and stereo matching for
artographic feature extraction.
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 14(2):214-238, 1992.
- 75
- V. Gerdes.
Modular rendering tools [online] http://www-student.informatik.
uni-bonn.de/gerdes/MRTStereo/, 2001.
- 76
- D. Scharstein and
R. Szeliski.
Stereo vision research page [online] http://cat.
middlebury.edu/stereo/data.html, 2006.
- 77
- K. N. Kutulakos and
S. M. Seitz.
A theory of shape by space carving.
Int. J. Computer Vision,
38:199-218, 2000.
- 78
- A. Torralba.
Modeling global scene factors in attention.
J. Optical Society of America,
20A:1407-1418, 2003.
- 79
- S. Birchfield and
C. Tomasi.
A pixel dissimilarity measure that is insensitive to image sampling.
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 20(4):401-406, 1998.
Footnodes
- ...
network2.1
- In application to a
much simpler problem of binary labelling where such approach leads
to an exact solution, the maximum-flow / minimum-cut technique was
proposed first in [44].
- ...
seen2.2
- Scene assumptions enable the matching
regions to be
delimited. Assuming no ``out-of-image" matching eliminates the lower
right triangle. Restricting a closest distance (or maximum
disparity) eliminates much of the upper left. However, plenty of
candidate matches remain!
- ... 3.1
- To generate that noise, the normal
centred deviation
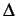 with
distribution
with
distribution 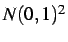 is produced
from a uniformly distributed
random deviation and converted to the normal deviation with
distribution is produced
from a uniformly distributed
random deviation and converted to the normal deviation with
distribution 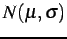 using an
obvious relationship using an
obvious relationship 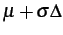 . .
- ...
NCSM-SDPS)5.1
- NCSM-SDPS has
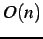 complexity because SDPS is
linear in the image width ( complexity because SDPS is
linear in the image width (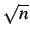 ) and repeated at each row
( ) and repeated at each row
(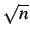 )
for image size )
for image size 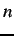 ;
the complexity of NCSM-ITER is ;
the complexity of NCSM-ITER is 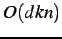 ,
where ,
where 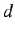 is the
range of disparities and is the
range of disparities and 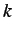 is the
number of iterations.
is the
number of iterations.
|