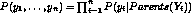Next: Inference
Up: Bayesian Learning
Previous: A Bayesian Belief Network
- Each variable is represented by a node and has two types of
information specified.
- Arcs representing the assertions that the variable is
conditionally independent of its nondescendents given its immediate
predecessors (i.e., Parents).
 is a descendent of
is a descendent of  if there is a
directed path from
if there is a
directed path from  to
to  .
. - A conditional probability table describing the probability
distribution for that variable given the values of its immediate
predecessors. This joint probability is computed by
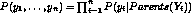
-
 is conditionally independent of its nondescendents
is conditionally independent of its nondescendents
 and
and
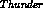 given its parents
given its parents 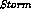 and
and 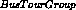
-
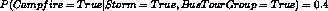
- Also notice that
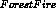 is conditionally independent of
is conditionally independent of
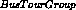 and
and 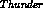 given
given 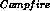 and
and 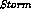 and
and 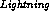
- Similarly,
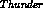 is conditionally independent of
is conditionally independent of
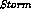 ,
, 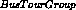 ,
, 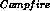 , and
, and 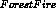 given
given
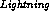 .
. - BBNs are a convenient way to represent causal knowledge. The fact
that
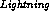 causes
causes 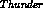 is represented in the BBN by
the fact that
is represented in the BBN by
the fact that 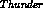 is conditionally independent of other
variables in the network given the value of
is conditionally independent of other
variables in the network given the value of 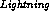 .
.
Patricia Riddle
Fri May 15 13:00:36 NZST 1998
 is a descendent of
is a descendent of  if there is a
directed path from
if there is a
directed path from  to
to  .
.