



Next: An Example
Up: Bayesian Learning
Previous: Gibbs Algorithm
- results comparable to ANN and decision trees in some domains
- Each instance
 is described by a conjunction of attribute
values and the target value
is described by a conjunction of attribute
values and the target value 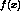 can take any value from a set
can take any value from a set
 . A set of training instances are provided and a new instance is
presented and the learner is asked to predict the target value.
. A set of training instances are provided and a new instance is
presented and the learner is asked to predict the target value. -
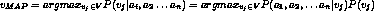
-
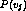 is estimated by the frequency of each target value in
the training data
is estimated by the frequency of each target value in
the training data - cannot use frequency for
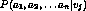 unless
we have a very,very large set of training data to get a reliable
estimate
unless
we have a very,very large set of training data to get a reliable
estimate - naive Bayes assumes attribute values are conditionally
independent given the target value -
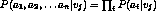
- Naive Bayes classifier:
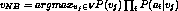 , where
, where 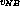 denotes the target value
denotes the target value -
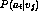 can be estimated by frequency
can be estimated by frequency - when conditional independence assumption is satisfied the naive
Bayes classification is a MAP classification
- naive Naive Bayes entails no search!!
Patricia Riddle
Fri May 15 13:00:36 NZST 1998