



Next: Optimal Policy
Up: Reinforcement Learning
Previous: Reinforcement Learning Problems
- based on Markov decision processes (MDP)
- At each time step
 , the agent senses a current state
, the agent senses a current state
 and chooses an action
and chooses an action  and performs it. The
environment responds with a reward
and performs it. The
environment responds with a reward 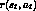 and by producing
the succeeding state
and by producing
the succeeding state 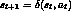 .
. - The functions
 and
and  are part of the environment and not necessarily
known to the agent. They also only depend on the current state and action.
are part of the environment and not necessarily
known to the agent. They also only depend on the current state and action. - We only consider finite sets
 ,
,  and deterministic
functions, but these are not required.
and deterministic
functions, but these are not required. - Learn a policy
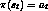 , with the greatest cumulative reward over
time.
, with the greatest cumulative reward over
time. -
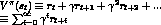 discounted
cumulative reward
discounted
cumulative reward - where
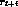 is generated by beginning at state
is generated by beginning at state  and
repeatedly using policy
and
repeatedly using policy  to select actions,
to select actions, -
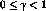 is a constant that determines the
relative value of delayed versus immediate rewards - if
is a constant that determines the
relative value of delayed versus immediate rewards - if 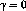 only immediate reward is considered, as
only immediate reward is considered, as  moves closer to 1
future rewards are given more emphasis.
moves closer to 1
future rewards are given more emphasis. -
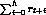 finite horizon reward
finite horizon reward -
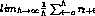 average reward
average reward - We will only focus on discounted cumulative reward!
Patricia Riddle
Fri May 15 13:00:36 NZST 1998