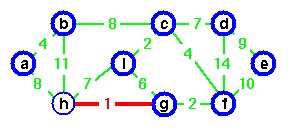
Either g or h could be the representative,
g chosen arbitrarily.
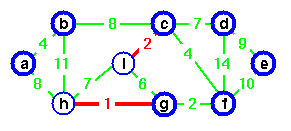
c chosen as representative for second.
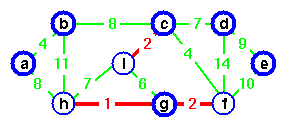
Add it, choose g as representative.
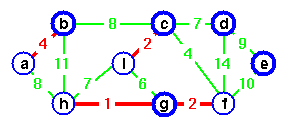
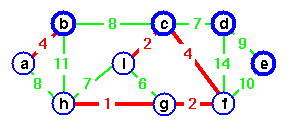
merging two trees.
c is chosen as the representative.
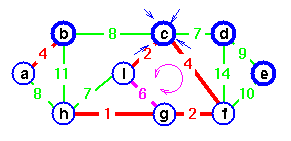
but a cycle would be created.
c is the representative of both.
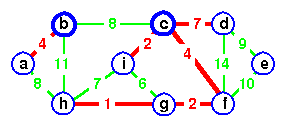
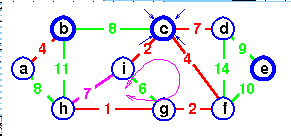
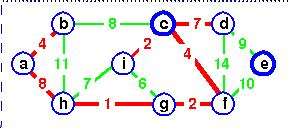
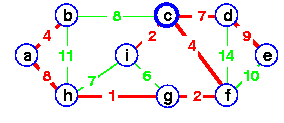
Add de instead
to complete the spanning tree -
all trees joined,
c is sole representative.
 , 1998
, 1998