![]()
The systems development life cycle consists of four foundation phases; planning, analysis, design and implementation. A methodology is a formalized approach to implementing the SDLC, which have formal standards used by consultants and organizations that develop their software in-house. Over time SDLC methodologies have evolved as project teams gain a better understanding of developing software
Structured Design
There are many different approaches to developing a software system. The classic example is the structured design or as it is commonly referred to as the waterfall lifecycle. This methodology takes the approach of a formal step by step approach to developing a system, where the team moves on to the next phase only when the previous phase is completed. An analogy used to describe this methodology is going down a waterfall.
This approach introduced the use of modeling of data and business processes
The advantage of the structured design is that the system scope is defined long before the programming aspect of the development begins; this minimizes the changes that can be made to the scope of the system.
The disadvantage of this approach is the fact that there is a lot of documentation; this can result in overlooking important aspects of the system, which can result in a high cost of re- programming of the system if the system has already been implemented. There is long time period between the requirements gathering and introducing the system to the users, which results in the loss of enthusiasm by the users to adopt the new system and there may even be the possibility that the business process may have changed since the requirements gathering phases, which would result in restarting the entire development process.
Rapid application development (RAD)
In this approach the SDLC is adjusted so a certain portion of the system is developed very rapidly earlier on in the development life cycle, this allows the users to sample a working version, which could potentially be part of the final system. This methodology is completed in a very structured environment, which gives the users and the developers to gain a better understanding of the business process that they are trying to model.
Rapid-application development emphasizes the use of CASE tools and computer tools, which help speed up the processes in the SDLC and improves the quality of the system that is being developed.
The disadvantage of this approach is the difficulty in managing the users expectations, because there are many tools that aid a project team in developing the software, which results in a drastic change in what the users want. The improvement in modeling results in the increase in systems requirements which can result in scope creep.
Within RAD, there are different methodologies such as process centered, data centered or object oriented, that follow the basic approaches of the three categories stated below.
Phased Development
This prototyping technique deals with building different versions of the system, which allows the users to interact with the system as soon as possible. The first version has the core functions which represents the core business processes. In this approach, the overall system concept is identified in the analysis phase and the core functions is designed and implemented into the first version. There is an iterative cycle between analysis, design and implementation for every version of the system. The project team will add more features to each of the subsequent versions until all of the relevant business processes are captured.
Prototyping
This methodology executes the analysis, design and implementation phases at the same time. These phases are completed in an iterative process, as in the phased development, until the system is completed and handed over to the users. The basics of the planning and analysis are completed in a short period of time, after which a ‘quick and dirty’ prototype is completed which has the fewest of features. Analysis, design and implementation phases of the prototype are re-visited with the input of users. This process is completed numerous times until all the features of the system have been identified and implemented.
Throw- away prototyping
This approach is very similar to the prototyping development, which balances the benefits of completing the analysis and design phases thoroughly, but with the advantage of using prototypes to refine key issues before a system built. Each new system is built from scratch, while the previous version of the prototype is discarded. This method may take longer than prototyping but usually produces more stable and reliable systems.
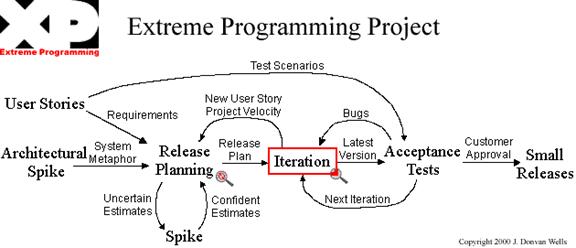
Extreme Programming
This system development approach is based on 4 fundamental values, which are simplicity, communication, feedback, and courage. The aim of this approach is to bring the entire project team and users together set the requirements, identify the priorities steer the project on the right path from the beginning.
Extreme programming aims to address two important questions for software development, which is predicting what tasks will be accomplished by a specified due date and then determining what to do next. This is different to exactly specifying what will be needed and how long it will take to complete. There are two planning steps in Extreme Planning that tries to address the questions stated earlier.
Proposed System Progress Company Background Our bid for 340 What's ERP Home Methodologies in use Application Screenshot