The search algorithm is used to plan the route between two locations. Our aim of the search algorithm are implemented an efficient search and the planned route has balances between driving distance and minimal number of turns.
In this project, each group member implements a search algorithm. Based on the performances and quality of results, we decides which algorithms are the most suitable algorithm to use for the route planning. The algorithm I was implemented Dijkstraˇ¦s algorithm, A* search, Hierarchical search base on A* and island search base on A* are implemented in this project.
Dijkstraˇ¦s algorithm is one of the several algorithm finds the shortest paths from the source node to all other nodes in a graph with nonnegative arc lengths. In Dijkstraˇ¦s algorithm each node maintains a distance label and each node can be classify as either permanently labeled (or permanent) or temporarily labeled (or temporary). The value of distance label d(i) at a node represents distance from source node to that particular node. A permanent label represents the node is finished and it distance label is the shortest distance to the source node. The search works as follow.
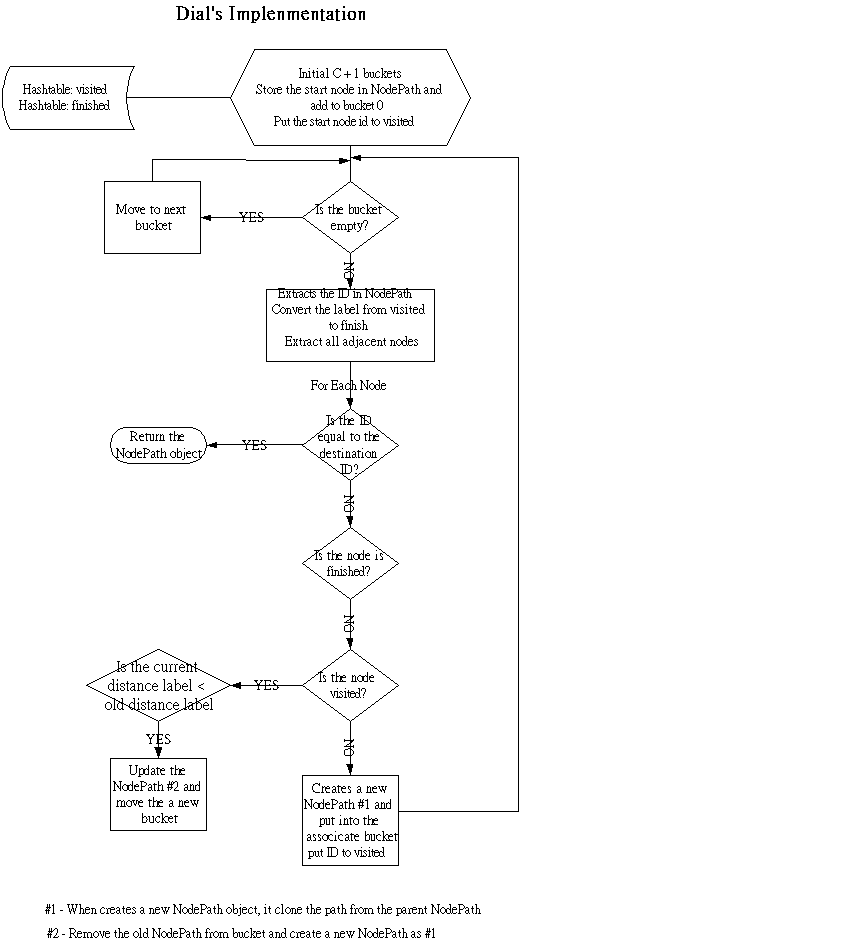
Dial's implementation is a Dijstra's algorithm implemented on a different data structure. Nodes store in buckets to reduce the node selections time Buckets are sets arranged in a sorted fashion, a bucket only stores the node with a same distance label In Dial's implementation, bucket k contains all temporarily labeled nodes whose distance labels are equal to k. Buckets numbered 0, 1, 2, 3, ...C, are checked sequentially until the first nonempty bucket is identified. Each node contained in the first nonempty bucket has the minimum distance label
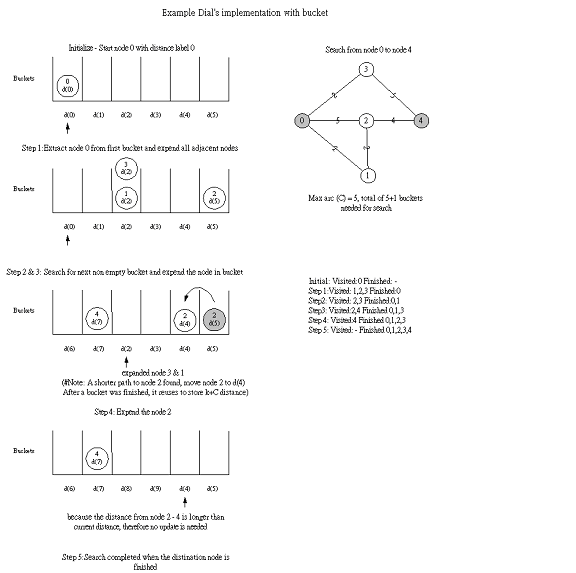
Dial's search algorithm was implemented in this project. Below is a flow chart describes the Dial’s implementation.
